The language of sleep can be confusing. Adenosine? Melatonin? Hypnagogic Jerk? We have compiled a comprehensive dictionary of sleep terminology to help you navigate the science.
A
Adenosine: A neurotransmitter that builds up in the brain during wakefulness, creating “Sleep Pressure”. Caffeine works by blocking adenosine receptors.
Apnea: A condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts.
Read more.
C
Circadian Rhythm: The body’s natural 24-hour internal clock that regulates the sleep-wake cycle based on light and darkness.
Cortisol: The “stress hormone” that should peak in the morning to wake you up and drop at night. High levels at night cause insomnia.
G
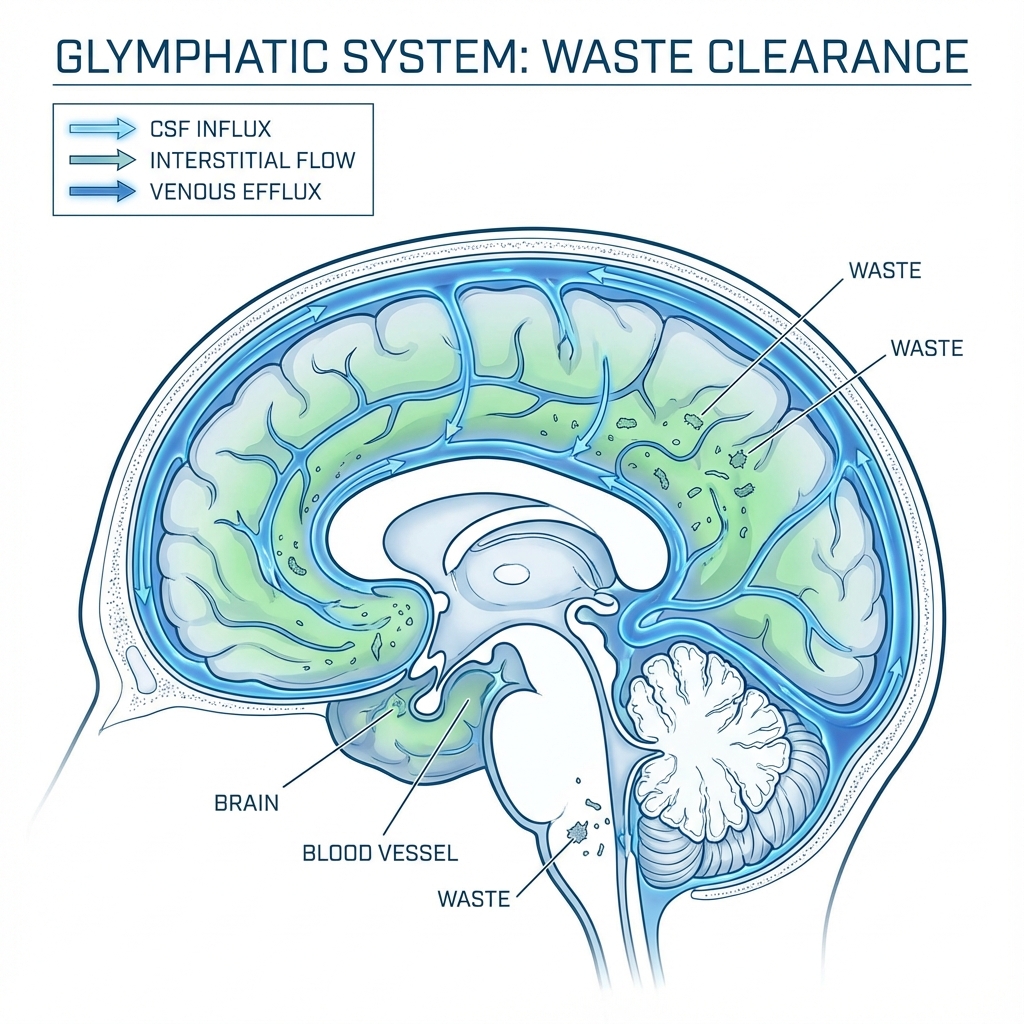
Glymphatic System: A waste clearance pathway in the brain that is most active during deep sleep, flushing out toxins like beta-amyloid.
H
Hypnic Jerk: An involuntary twitch (feeling like falling) that occurs just as a person is beginning to fall asleep.
L
Lucid Dreaming: A state where the dreamer is aware they are dreaming and can control the dream text.
M
Melatonin: A hormone produced by the pineal gland in response to darkness that signals the body to sleep.
R
REM (Rapid Eye Movement): The stage of sleep associated with dreaming, memory consolidation, and emotional processing.
S
Sleep Debt: The cumulative effect of not getting enough sleep over a period of time.
Read more.
Sleep Hygiene: Habits and practices that are conducive to sleeping well on a regular basis.
W
White Noise: A consistent noise containing all frequencies across the spectrum of audible sound in equal measure. Used to mask disruptive sounds.
B
Blue Light: Artificial light emitted by screens that suppresses the secretion of melatonin, tricking the brain into thinking it is still daytime.
Bruxism: The involuntary grinding or clenching of teeth during sleep, often associated with stress or misaligned jaws.
C
Chronotype: The genetically determined natural inclination of your body to sleep at a certain time (e.g., Night Owls vs. Early Birds).
Find yours here.
H
Hypnogram: A graph that visualizes the stages of sleep (REM, Light, Deep) over the course of the night, used in clinical sleep studies.
L
Latency (Sleep Onset Latency): The amount of time it takes to fall asleep after getting into bed. A healthy latency is between 10 to 20 minutes.
M
Microsleep: A fleeting, uncontrollable moment of sleep that lasts anywhere from a fraction of a second to 10 seconds, often occurring during sleep deprivation.
N
NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement): The collective name for Stages 1, 2, and 3 (Deep) of sleep. This is where physical restoration occurs, distinct from the mental restoration of REM.
P
Parasomnia: A category of sleep disorders that involve abnormal movements or behaviors, such as sleepwalking, sleep talking, or sleep terrors.
S
Sleep Architecture: The structural organization of normal sleep, consisting of cycles of NREM and REM sleep phases.
Read the full guide.
Z
Zeitgeber: A German term meaning “Time Giver”. Any external cue (like sunlight, meals, or temperature) that synchronizes the body’s biological rhythms to the Earth’s 24-hour cycle.